Picture this: a bustling commercial office, where teams collaborate, phones ring, and the hum of productivity is palpable.
Yet, amidst this hive of activity, there’s a meeting room, enclosed in clear glass, where critical discussions occur in complete silence, undisturbed by the surrounding buzz.
In modern offices, where space optimization and aesthetics are paramount, transparent glass dividers have become the go-to for demarcating meeting areas.
But the true genius lies in employing soundproofing glass – offering a blend of visual connectivity and acoustic privacy.
So, how do these transparent barriers manage to mute the outside world while still appearing almost invisible?
Let’s dive deeper into this architectural marvel, exploring its role in revolutionizing commercial office spaces.
What Is Soundproofing Glass?
In our increasingly urbanized world, noise pollution has emerged as a significant concern, impacting our mental and physical well-being. Soundproofing glass has been developed as a response to this challenge.
At its essence, soundproofing glass is not just a product but a sophisticated fusion of science and engineering designed to significantly diminish the intrusion of external noise.
While the primary function of standard glass is to offer transparency and barrier functions, soundproofing glass takes this a step further.
It seamlessly integrates aesthetics with functionality. Not only does it provide the clarity and transparency expected of glass, but it also acts as a sentinel, guarding against the cacophony of the outside world.
The beauty of soundproofing glass lies in its versatility. It can be as clear and transparent as regular glass or tinted for added privacy or aesthetic appeal.
Furthermore, advancements in technology have enabled the production of soundproofing glass that also offers UV protection, thermal insulation, and enhanced safety and security features.
How Does Soundproofing Glass Work?
To truly appreciate the marvel that is soundproofing glass, one must delve into the principles underpinning its functionality. Sound waves are essentially energy.
When these waves hit a surface, they cause vibrations. It’s these vibrations that our ears pick up and interpret as sound.
Regular glass can vibrate more easily with the impact of sound waves, transferring most of that sound energy from one side to the other.
Soundproofing glass, however, is designed to disrupt this energy transfer. It does so in a variety of ingenious ways.
The first line of defense is the increased mass. It’s a fundamental principle of acoustics that thicker, denser materials are harder for sound to penetrate.
By making the glass thicker or by adding additional layers, soundproofing glass enhances its resistance to sound wave energy.
But the marvel doesn’t stop at mere thickness. The layers within soundproofing glass play a crucial role. Special laminates or materials sandwiched between the glass panes act as dampers.
These materials absorb and dissipate the energy of the sound waves, preventing them from passing through.
Modern soundproofing glass often incorporates not just two but multiple layers in its design. The spaces between these layers can be vacuum-sealed or filled with inert gases like argon or krypton.
These gases are denser than air and further impede the transfer of sound.
This multi-layered approach ensures that by the time the sound has navigated its way through the various defenses, its energy is significantly diminished, resulting in a much softer, barely audible sound on the other side.
Benefits Of Using Soundproofing Glass

The application of soundproofing glass goes beyond mere noise reduction. In today’s world, where distractions are plentiful, the ability to control one’s environment can have profound effects on well-being and productivity.
In residential settings, the peace and tranquillity afforded by soundproofing glass can transform living spaces.
Imagine a home where the blaring horns, the distant rumble of trains, or the incessant hum of traffic are but faint whispers.
Such a space becomes a haven, allowing for restful sleep, focused work, or simply a peaceful retreat from the hustle and bustle of the outside world.
Beyond the tangible benefits, there’s a psychological advantage to using soundproofing glass.
Knowing that one’s privacy is secured, that conversations won’t be overheard, and that one’s moments of quiet reflection won’t be interrupted can significantly reduce stress and enhance mental well-being.
Moreover, in a world increasingly conscious of energy consumption and its environmental impact, soundproofing glass offers another significant benefit: energy efficiency.
Its insulative properties mean that homes and buildings lose less heat in the winter and stay cooler in the summer.
This reduced strain on heating and cooling systems can lead to substantial energy savings, cutting costs, and reducing carbon footprints.
Common Applications Of Soundproofing Glass

Soundproofing glass’s utility spans a diverse array of sectors, reflecting its versatility and the universal need for quiet and tranquility in various contexts.
In the realm of residential architecture, soundproofing glass has revolutionized home design, especially in urban and suburban areas.
As cities expand and the space between homes shrinks, privacy and noise reduction become paramount.
Homes near schools, playgrounds, and parks, where the joyful cacophony of children playing can become a disturbance, greatly benefit from soundproofing solutions.
Equally, homes near transport hubs, such as bus depots, train stations, or even airports, can find solace from the constant barrage of noise.
Commercial spaces, from towering skyscrapers to boutique offices, have also embraced soundproofing glass.
The modern workspace, with its emphasis on collaboration and open-plan design, needs effective noise management solutions.
Meeting rooms equipped with soundproofing glass ensure confidentiality.
Open spaces, where employees engage in focused work or make critical phone calls, benefit from the reduction in ambient noise, fostering a more productive environment.
Entertainment venues, like theaters and concert halls, require pristine acoustics. Soundproofing glass ensures that external noises, from the hum of traffic to the chatter of crowds, don’t infiltrate these spaces.
Similarly, recording studios, where even the faintest of sounds can disrupt a recording, rely heavily on soundproofing technologies.
Educational institutions, particularly those in bustling urban environments, utilize soundproofing glass to create optimal learning environments.
Classrooms free from external distractions allow for better concentration and improved learning outcomes.
Industrial settings present unique challenges. Factories and manufacturing units are often hubs of noise, with machinery and equipment operating continuously.
Administrative offices, control rooms, or even break rooms within these facilities can utilize soundproofing glass to carve out pockets of calm amidst the din.
Types Of Soundproofing Glass
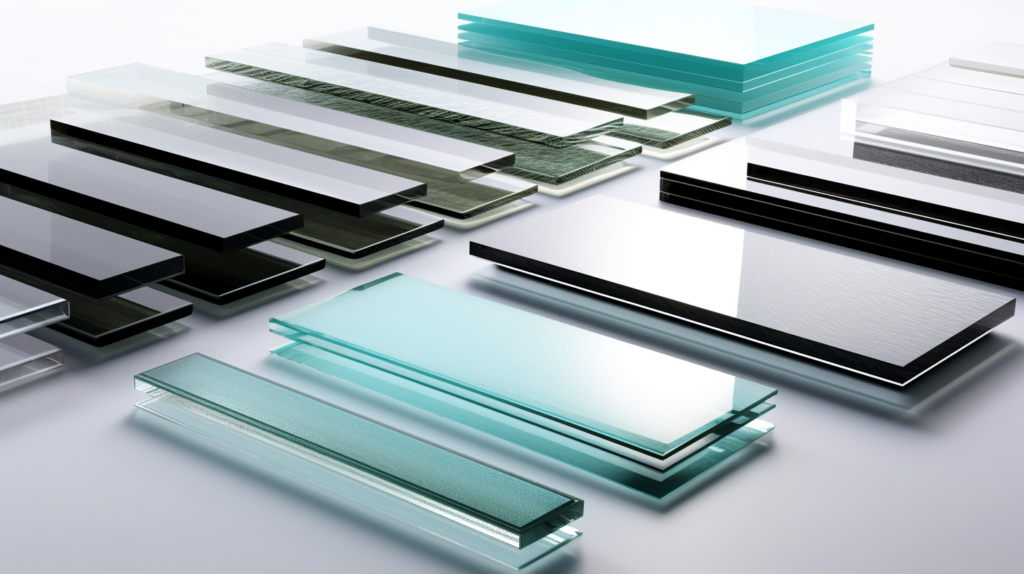
The intricacies of soundproofing glass are manifold, with various types and designs catering to different needs and specifications.
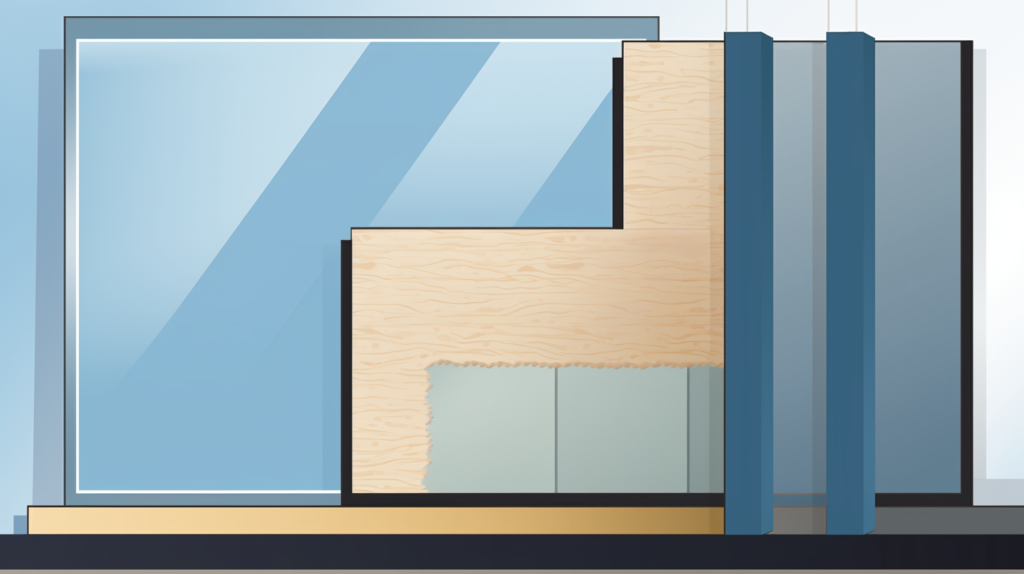
Laminated glass stands out for its resilience and effectiveness. It typically involves two or more sheets of glass bound together with an interlayer, often made of resin or plastic.
This composition not only bolsters its soundproofing capabilities but also enhances its safety properties. In the event of breakage, the shards adhere to the interlayer, preventing potential injuries.
Incorporating Acoustic PVB, or Polyvinyl Butyral, represents another significant advancement in soundproofing glass technology.
This resin, when used as an interlayer, offers exceptional sound damping. Its unique properties absorb and dissipate sound energy, making it an integral component in many soundproofing applications.
The world of glazing offers even more options.
Double and triple glazing techniques involve using two or three sheets of glass, respectively. These sheets are separated by spaces, often filled with inert gases like argon or krypton, which are less conducive to sound than regular air.
This design significantly diminishes sound transmission, making it a popular choice for both residential and commercial applications.
Limitations And Alternatives

While soundproofing glass is a marvel of modern engineering, it’s essential to recognize that no solution is without its limitations.
As with all products, understanding these limitations ensures that expectations are aligned with reality.
One of the primary challenges is achieving complete sound isolation.
While soundproofing glass can drastically reduce noise levels, certain frequencies or particularly loud sounds might still penetrate.
It’s crucial to understand that soundproofing doesn’t equate to total silence but rather a significant reduction in ambient noise.
Ventilation can also pose challenges. The properties that make soundproofing glass effective against noise—its sealed design and multiple layers—also make it less permeable to air.
In settings where fresh air circulation is crucial, alternatives or supplementary solutions might be needed.
This leads to the exploration of alternative soundproofing methods. Depending on the specific needs and constraints of a space, other soundproofing materials and techniques can be considered.
Acoustic panels, for instance, offer effective soundproofing for walls and ceilings.
For those not looking to replace their windows, soundproofing curtains or drapes can provide a degree of noise reduction.
These fabrics, often dense and heavy, act as barriers to sound, making them a cost-effective alternative to soundproofing glass.
When considering soundproofing solutions, it’s crucial to evaluate the specific requirements of a space.
This involves understanding the sources and types of noise, the desired level of sound reduction, and any other specific needs or constraints.
By doing so, one can choose the most effective and appropriate solution, ensuring a quieter and more serene environment.
Conclusion
In an age where urban sprawl and noise pollution are ever-increasing challenges, the need for effective soundproofing solutions has never been more pronounced.
Soundproofing glass emerges as a beacon of innovation, marrying science, engineering, and design to offer respite from the relentless clamor of the outside world.
Its applications span from the intimacy of our homes to the vast expanse of commercial and industrial spaces, proving its versatility and universal appeal.
While it isn’t without its limitations, the advantages it brings to our daily lives are undeniable.
As we continue to seek harmony in our surroundings, soundproofing glass stands as a testament to human ingenuity, ensuring that, amidst the noise, we can always find a pocket of tranquility.
Frequently Asked Question (FAQ)

How effective is soundproof glass?
Soundproof glass is highly effective in reducing noise pollution. It can diminish external noise levels by up to 90%, depending on the thickness of the glass and the type of interlayer used.
The overall effectiveness also depends on the quality of installation and the presence of any gaps or weak points in the window or wall structure.
What is the difference between sound proof glass and normal glass?
Normal glass typically consists of a single pane that offers basic barrier functions, while soundproof glass involves multiple layers of glass and special interlayers designed to absorb and dampen sound.
Soundproof glass is also generally thicker than normal glass and may contain gases like argon between its layers to further reduce sound transmission.
Is soundproof glass breakable?
Yes, soundproof glass is breakable as it is still glass, although it is tougher than standard single-pane glass due to its multi-layered structure and lamination.
It can withstand greater impact without shattering easily, and if broken, the interlayer keeps the shards in place, reducing the risk of injury.
What Is Soundproofing Glass Used For?
Soundproofing glass is used in various settings where noise reduction is desired.
This includes residential areas for peace and quiet, commercial spaces like offices and meeting rooms for improved productivity, educational institutions for better learning environments, recording studios for clear sound capture, and healthcare facilities for patient comfort.
What Is Soundproofing Glass Price?
The price of soundproofing glass varies widely based on factors like thickness, size, type of interlayer, and additional features such as UV protection or tinting.
On average, it can cost between $10 to $50 per square foot, with high-end options exceeding these figures.
How Thick Is Soundproof Glass?
Soundproof glass thickness can range from around 1/4 inch to over 1 inch.
The most common configurations are double-glazed units with panes around 1/4 inch thick each, separated by a space filled with air or inert gas.
Thicker glass offers better soundproofing but comes at a higher cost and requires stronger support due to increased weight.
Is Toughened Glass Soundproof?
Toughened glass, also known as tempered glass, is designed to be more impact-resistant than regular glass but it is not inherently soundproof.
However, toughened glass can be incorporated into a soundproof glass system, such as in double glazing, where it can help reduce noise when combined with other sound-dampening materials.
