If your outdoor oasis feels more like a noisy construction zone, it may be time to explore some soundproofing solutions.
With careful planning and design, you can effectively reduce unwanted sounds for a tranquil backyard retreat.
Let’s dive into some of the top techniques for soundproofing outdoor spaces.
Why Soundproof an Outdoor Area

Creating an outdoor living space provides a peaceful sanctuary for relaxation and entertainment.
However, noise pollution from nearby traffic, machinery, construction, voices and other sources can disrupt your ability to enjoy the space. Soundproofing is important for several key reasons:
Reduced Stress – Excess noise triggers the body’s stress response. Constant loud disruptions raise blood pressure and heart rate, tensing muscles and increasing anxiety.
Soundproofing eliminates this wear and tear from noise pollution.
Improved Relaxation – The natural sounds of breezes in trees or a water feature enhance relaxation. Noise reduction enables you to fully benefit from the restorative effects of an outdoor escape.
Increased Privacy – Carrying conversations or enjoying quiet activities is difficult with excessive noise intrusion. Sound barriers provide seclusion and confidentiality.
Healthier Hearing – Prolonged loud noise damages hearing over time. Soundproofing protects hearing health and prevents accelerated hearing loss.
Better Sleep Quality – Outdoor noise filtering into bedrooms reduces sleep quality, harming health. Sound barriers allow windows to stay open for fresh air without noise disruption.
Enhanced Property Value – Outdoor living spaces are more usable and desirable with effective noise reduction. Soundproofing improvements can increase resale value.
With so many benefits, soundproofing an outdoor area is a worthwhile investment. The ability to fully enjoy exterior spaces free of noise pollution has huge quality of life advantages.
Careful planning and design ensures your noise reduction solutions are both effective and aesthetically pleasing.
Using Acoustic Fence Panels for Noise Reduction

Acoustic fence panels, also known as noise barrier fences or noise-reducing fences, are specifically designed to absorb and block sound.
Installing these types of fences around a patio, yard, or other outdoor area can significantly reduce noise infiltration from surrounding environments.
Acoustic fence panels are constructed using sound-absorbing materials encased within weather-resistant outer layers.
The inner sound-absorbing core is typically made from dense, porous substances like fiberglass, melamine foam, recycled cotton, or open-cell polyurethane.
The outer shell is usually composed of plywood, metal, vinyl, or other durable materials.
This combination of sound-absorbing and weather-resistant properties makes acoustic fence panels ideal noise barriers for outdoor spaces.
Compared to regular wooden or vinyl fencing, acoustic fence panels with sound-absorbing cores can reduce noise by up to 20 decibels.
This is due to their ability to absorb a wide range of sound frequencies rather than simply reflecting sound back.
High, mid, and low-frequency noises are all attenuated as they pass through the porous inner material.
Acoustic fence panels work by using their sound-absorbent inner core to convert noise into heat energy as sound passes through the porous material.
The conversion of acoustic energy into thermal energy prevents the noise from continuing to travel to the other side of the fence.
This ability to absorb a broad spectrum of audible frequencies is what gives acoustic fence panels their exceptional noise reducing capabilities.
When installing acoustic fencing, overlapping seams and gaps should be avoided to prevent sound leaks. Panels can be custom cut to follow the contours of the area being soundproofed.
For maximum noise reduction, the fencing should be continuous and close to sources of noise pollution.
Placing acoustic barriers close to loud infrastructure like roads and railways reduces the distance sound has to travel before being absorbed.
The installation process for acoustic fencing is relatively straightforward. Posts are erected at the appropriate intervals, taking care that post holes are sunk deeply enough to firmly anchor the fence line.
After posts are in place, the acoustic panels are attached using screws or other mounting hardware. Panels should be installed without any spaces or cracks that would compromise noise absorption.
For a clean look, trim pieces may be used to cover seams.
Maintenance needs for acoustic fencing are generally minimal. The exterior should be periodically washed to prevent dirt buildup that could reduce sound absorption.
Panels made from molded plastics or metal may never need repainting, while wood-surfaced versions will eventually require refinishing.
Checking for and repairing any cracks, gaps, or holes is important to maintain sound insulating performance. Any weathering or physical damage that occurs over time should be promptly fixed.
Planting Natural Sound Barriers
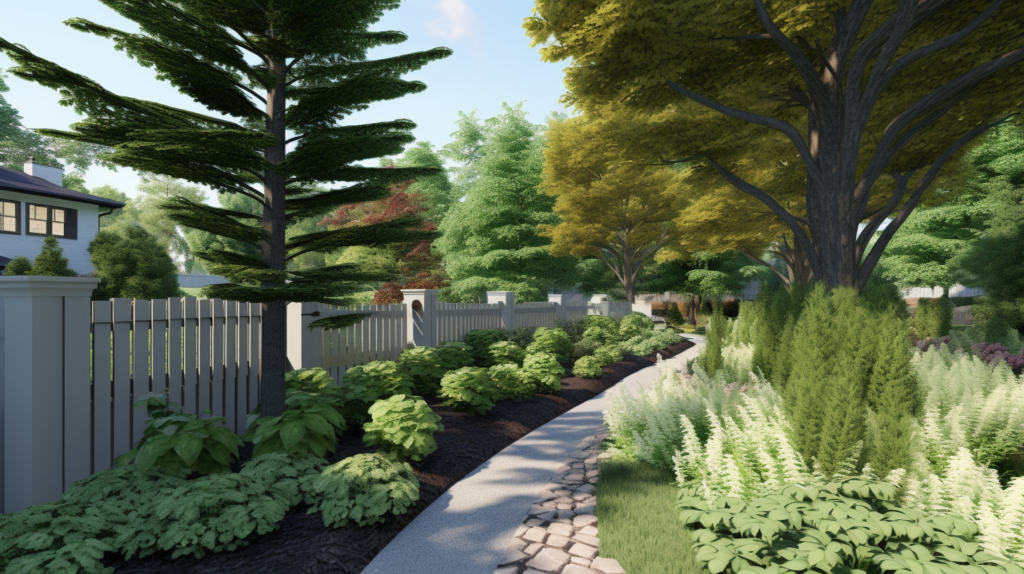

In addition to constructed barriers, carefully planned landscaping can also help absorb and block unwanted noise.
Trees, shrubs, trellises, and hedges strategically placed around an outdoor living area create natural sound buffers that softly diffuse sound.
Optimal plant choices for noise reduction have dense, evergreen foliage. Conifers like arborvitae, yews, and junipers work exceptionally well as sound-absorbing greenery.
Broadleaf evergreen shrubs such as boxwood, laurel, and holly also perform effectively as noise barriers.
Deciduous trees with multiple trunks rather than single trunks are preferable, as they maintain a dense barrier even in winter.
There are several characteristics that make certain plant varieties well-suited for soundproofing.
Foliage density is key, as plants with compact branching patterns and small leaves absorb and scatter sound waves most effectively.
Evergreen species maintain noise-blocking foliage year round compared to deciduous plants that drop leaves seasonally.
Plants with fibrous or fuzzy leaves and needles also help absorb noises. Native, resilient species require less maintenance to keep in optimal shape.
When arranging natural sound barriers, the goal is to create an acoustic “wall” rather than distinct specimens. Plantings should be continuous rather than sparse or patchy.
For best results, use multiple rows with slightly overlapping foliage. This eliminates gaps that allow sound to pass through. Positioning plants close to noise sources causes more sound interception.
A good strategy for plant placement is to use smaller shrubs in front with increasing height and density toward the back.
This helps contour the planting into an effective sound barrier. Mixing a variety of plant types also improves noise absorption across frequencies.
Allow adequate spacing for growth to avoid overly thin vegetation.
Regular pruning and maintenance keeps plantings full, healthy, and effective as sound buffers. Dead branches or sparse areas should be filled in with additional plantings.
Using native species suited to the climate reduces maintenance needs long-term. An automated watering system may be advisable for maintaining even soil moisture vital for plant health.
Apply organic mulch around plantings to help retain moisture and nutrients.
Incorporating Water Features to Mask Noise
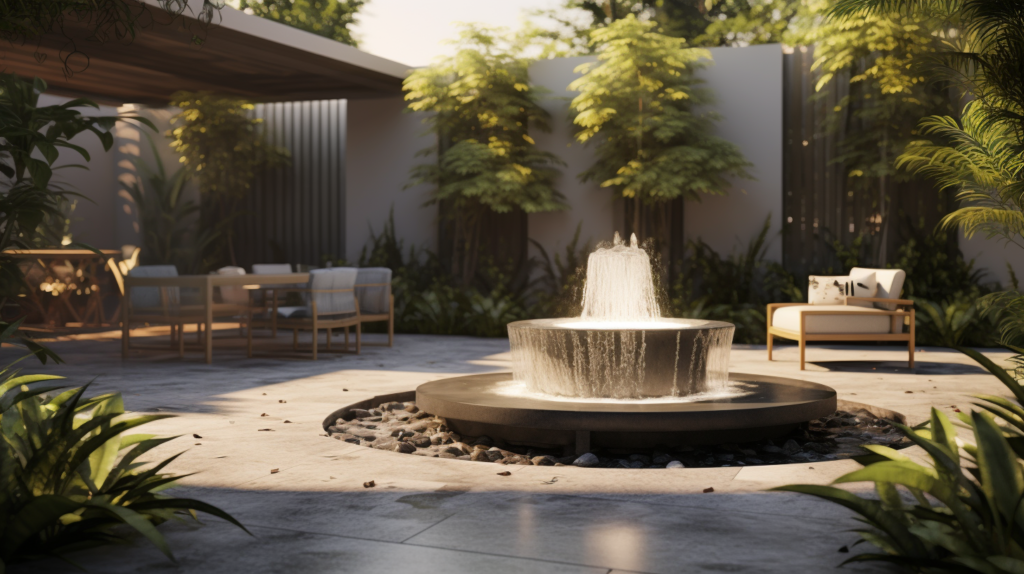

The soothing sounds of splashing or running water can be used to mask intrusive noises in outdoor spaces.
Whether it is a babbling stream, waterfall, or fountain, the ambient sounds of moving water have natural noise-masking abilities.
Small, self-contained tabletop fountains are an easy way to add calming water sounds to patios or decks. The bubbling noise helps cover unwanted sounds at close range.
Larger freestanding water features range from simple spouting urns to elaborate multi-tiered cascades. The splashing and rumbling provides louder masking volume.
For spaces where installation is possible, running water elements like backyard streams are especially effective at providing steady, natural white noise.
When selecting and placing a water feature, consider the type and volume of unwanted noises that need masking.
Choose designs where the cascading, gurgling, or running sounds are loud enough to cover disruptive noises.
Position the water feature as close as feasible to the source of noise pollution. Include lighting to create nighttime visual appeal and noise reduction.
If noise levels are not sufficiently masked by a single water feature, installing multiple coordinated elements can increase sound coverage.
A trio of fountain urns or a mix of a bubbling rock fountain and small stream extends spatial masking across a larger area.
Amplifying the water sounds with carefully hidden speakers can also boost noise reduction.
Regular cleaning and maintenance keeps water features operating optimally. Pumps, tubing, and electric components require periodic inspection and occasional replacement of parts.
Algae growth and debris should be promptly removed from water surfaces and containers. Take steps like circulation, filtration, and sanitizing to prevent stagnation and mosquito breeding.
Building Soundproof Sheds
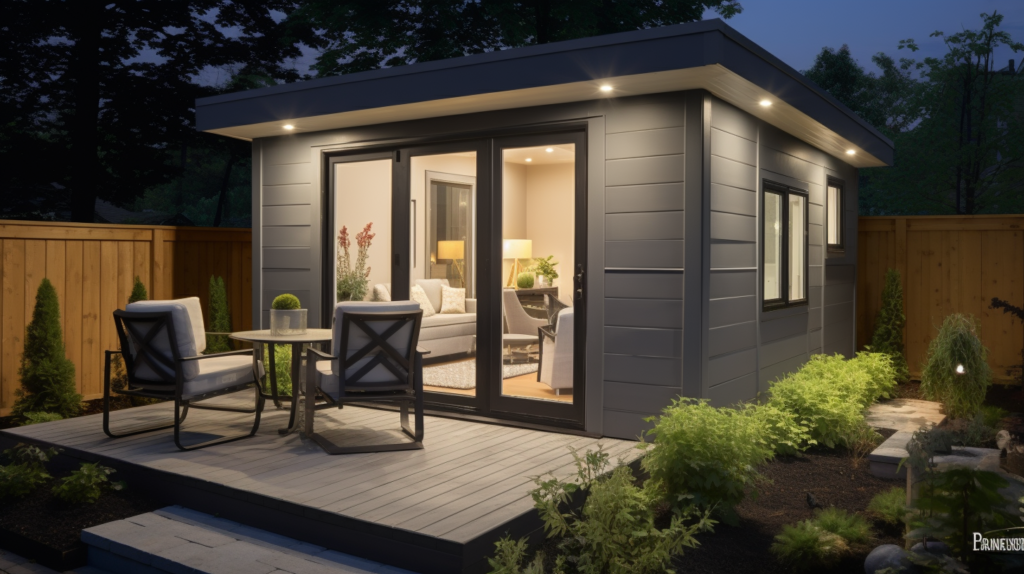

Adding a dedicated soundproof shed to your outdoor living space allows you to fully control noise while having an escape free of distractions.
Carefully designing and constructing a shed specifically for soundproofing creates an ideal noise-free sanctuary.
Using acoustically engineered building materials is key for maximum noise reduction. Fiber cement siding containing sound-absorbing fibers blocks noise penetration through walls and roofs.
Solid core doors with perimeter sealing prevent sound leaks at entry points. Acoustic caulking, insulation, and drywall further absorb sound.
Soundproof windows maintain visibility while preventing noise intrusion.
Choose construction materials with density and weight to add mass that impedes sound transmission. Double-pane windows with wide, staggered air gaps enhance acoustic insulation.
Sound-absorbent materials like acoustic tiles or foam panels on walls minimize reverberations within the interior space. Any vents should have baffles allowing airflow while blocking noise.
Position the shed to physically block primary noise sources. Face the opening away from dominant noise to prevent sound waves entering directly.
Place on a concrete slab for vibration dampening. Situate away from echoing surfaces that could reflect noise back. Follow construction best practices for an airtight, noise-sealed environment.
A soundproof shed creates the perfect distraction-free oasis to relax, work or pursue hobbies without noise disruption.
The investment into a fully noise-controlled structure pays dividends through vastly enhanced focus, productivity, and enjoyment within your private sanctuary space.
Understanding and Addressing Different Types of Outdoor Noise
The most effective soundproofing solutions are tailored to the specific types of noise affecting an outdoor area.
First identify the primary sources – nearby roads, railways, aircraft, construction, voices, machinery, etc. Understanding the characteristics of the sound helps determine optimal noise barriers.
Traffic noise contains a mix of low, mid and high frequencies.
The low rumble of large truck engines combines with sharp honks and higher-pitched whining of smaller vehicles into a full-spectrum cacophony.
Solid barriers like fences, walls, and berms help, along with white noise masking. Aircraft noise varies in intensity and also has a wide frequency range.
The drone of turbines and roar of takeoff and landing contains everything from deep rumbles to screeching highs.
Acoustic structures and panels often work better than landscaping. Neighbor noise is usually higher frequency, so dense plantings help absorb and block sounds more than solid fences.
Voices, music and clamor from yards, pools and patios can be softened and scattered by vegetation. Machinery like generators or construction equipment produces deeper, rumbling noise.
For low-pitch mechanical noise, mass and isolation tactics help reduce transmission.
Adapting solutions for the predominant frequencies of noise maximizes soundproofing. For lower-pitched sounds, barriers with more mass and vibration damping are preferable.
High-frequency noise is readily absorbed by porous materials and vegetation. Combining tactics covers all frequencies for mixed noise sources like roadways near airports.
Don’t focus only on the loudest components – reducing mid and high frequencies also significantly improves acoustic comfort.
Balancing Cost and Effectiveness in Soundproofing

Determining the most suitable soundproofing solutions involves balancing acoustic effectiveness against budget and aesthetic considerations.
Fortunately, there are options at every price point to drown out or reduce unwanted noise.
While solid construction fences provide maximum noise reduction, acoustic fence panels deliver substantial benefits at a lower cost.
Complementing fencing with strategically placed plantings boosts effectiveness for little added cost.
Less expensive, visually pleasing tabletop fountains can mask moderate noise levels. For more exposed areas with louder noise, a higher-priced cascading fountain becomes a worthwhile investment.
Landscaping with natural greenery is often the most budget-friendly noise reduction tactic. Establishing privacy shrubs and hedges serves dual aesthetic and sound absorbing purposes.
Even costly constructed screening can be phased in over time as budget allows. Mixing in inexpensive plantings maintains some noise reduction in the interim.
Ultimately, the long-term increase in relaxation, privacy, and usability of the outdoor space offsets the initial investment in quality soundproofing.
Any ability to enjoy outdoor living without disruption from intrusive noises is invaluable. Reducing unwanted noise also helps conserve hearing health and prevents stress.
Though requiring more upfront expenditure, choosing durable sound barriers with superior noise reduction provides lasting benefits that repay their cost many times over.
Conclusion
With creativity and the right combination of materials, outdoor spaces can be transformed from noisy trouble spots into peaceful refuges.
Whether constructing barriers or masking sound, quality soundproofing allows you to fully enjoy outdoor living areas free of disruptive noise.
Careful planning and smart design ensure your soundproofing solutions not only work effectively but also complement the aesthetic environment.
The investment pays continual dividends through vastly enhanced relaxation, entertainment, and privacy in your newly tranquil outdoor sanctuary.
