Do you have noisy neighbors or loud traffic sounds disturbing your home or office acoustics?
Using egg crate as makeshift acoustic panels seems like an easy fix, but its noise-dampening capacity is minimal despite the porous appearance.
Let’s take a closer look at the acoustic properties of egg crate to see why it falls short for effective sound absorption and noise control.
Does Egg Crate Effectively Function as Acoustic Treatment?
In short – no, egg crate alone does not effectively function as substantive acoustic treatment.
As we’ll explore more below, its capacity to absorb sound energy is low, allowing most noise to transmit through the thin plastic grid with little reduction.
Now let’s examine in detail why it fails to dampen ambient noise as well as purpose-built acoustic absorption panels.
What is Egg Crate?
Egg crate is a lightweight plastic material with a waffle-like grid structure that diffuses light.
It is most commonly used in fluorescent light fixture covers and drop ceilings to disperse light evenly across a room or workspace.
The open grid pattern gives egg crate a porous and layered design which seems like it could potentially absorb sound.
With its ribbed and slotted structure, many people wonder if using egg crate could dampen noise and work effectively as an affordable acoustic treatment option.
The ridges and openings give it a similar appearance to purpose-built sound absorbing wall and ceiling tiles.
However, appearances can be deceiving when it comes to the acoustic properties of materials.
Acoustic Properties of Egg Crate
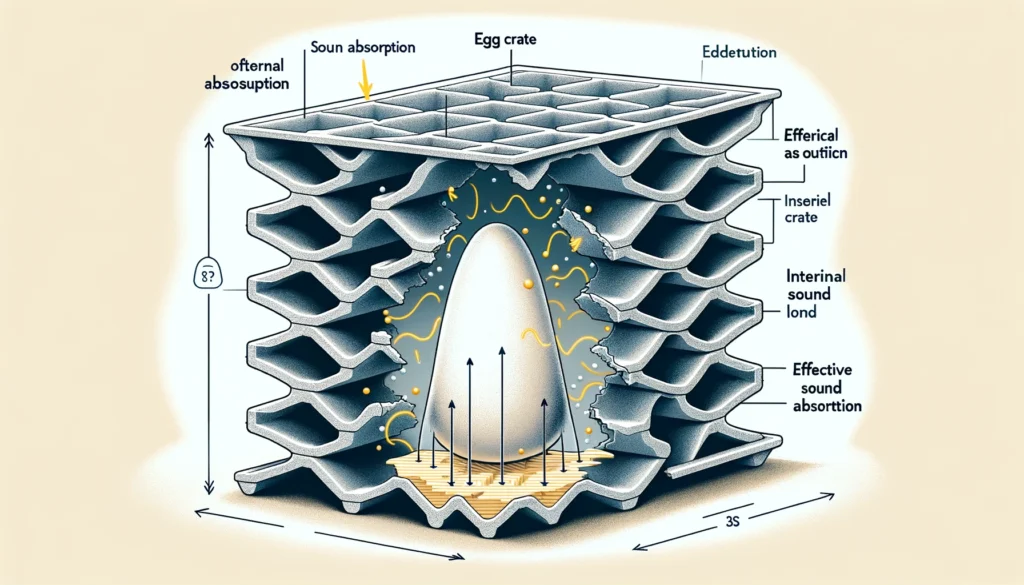
The overall design of egg crate, with its many openings backed by hollow airspace, allows sound waves to enter into the material rather than bounce and reverberate off a flat hard surface.
However, since egg crate is made from thin plastic rather than a dense noise-dampening material, most of these sound waves actually pass through the grid-like framework with little to no absorption occurring.
While the front face of an egg crate panel can provide some sound wave diffusion, scattering the noise in multiple directions, the lack of any notable internal sound absorption means the material does not actually dampen or reduce noise by much.
It does not effectively soak up acoustic energy like purpose-designed acoustic treatments and noise control products.
At best, plain plastic egg crate might make some insignificant impact on the reverberation time of higher frequency sounds due to minimal high frequency absorption.
But when it comes to meaningful noise reduction in any frequency range, plain egg crate does not deliver substantial acoustic panel performance.
Using Egg Crate as Acoustic Panels

Many people attempt to use egg crate as a cheap and easy acoustic solution, constructing basic sound absorbing panels out of the plastic grid material.
Pieces of egg crate are often mounted on walls or ceilings to mimic more effective acoustic tiles that feature sound-dampening properties.
However, plain egg crate fixed to a surface generally provides negligible real noise control.
Since egg crate itself barely absorbs any sound energy, acoustic panels made directly from the plastic material do not actually soak up much noise pollution.
Effective acoustic treatment requires materials with noise blocking mass, density, resonance damping characteristics, or embedded sound absorptive fillers.
Egg crate lacks these attributes, only consisting of hollow ribs of thin plastic that sound passes through readily.
The depth or thickness of an acoustic panel or noise barrier also impacts its effectiveness.
With egg crate being an extremely shallow surface, any minimal sound absorption happens only at this thin single layer.
Acoustic panels that work well use thicker sound-dampening materials and layers to catch sound waves before they bounce off the hard rear wall behind the insulation.
Alternatives for Acoustic Treatment

Instead of plain plastic egg crate with limited noise reduction capacity, there are many purpose-designed acoustical materials better suited for controlling sound transmission and reducing unwanted ambient noise pollution.
Effective acoustic panels typically contain sound-absorbing filler materials embedded internally that actively turn acoustic energy into minute levels of heat energy.
Materials like fiberglass, mineral wool, cotton insulation, open and closed cell foam, and recycled denim are excellent at damping noise via converting oscillating soundwaves into thermal energy.
Commercial companies sell well-constructed acoustic panels filled with layers of these noise-absorbing materials to successfully control room acoustics.
Absorptive panel solutions work by means of viscous losses and porous sound dissipation, proven physical properties egg crate lacks.
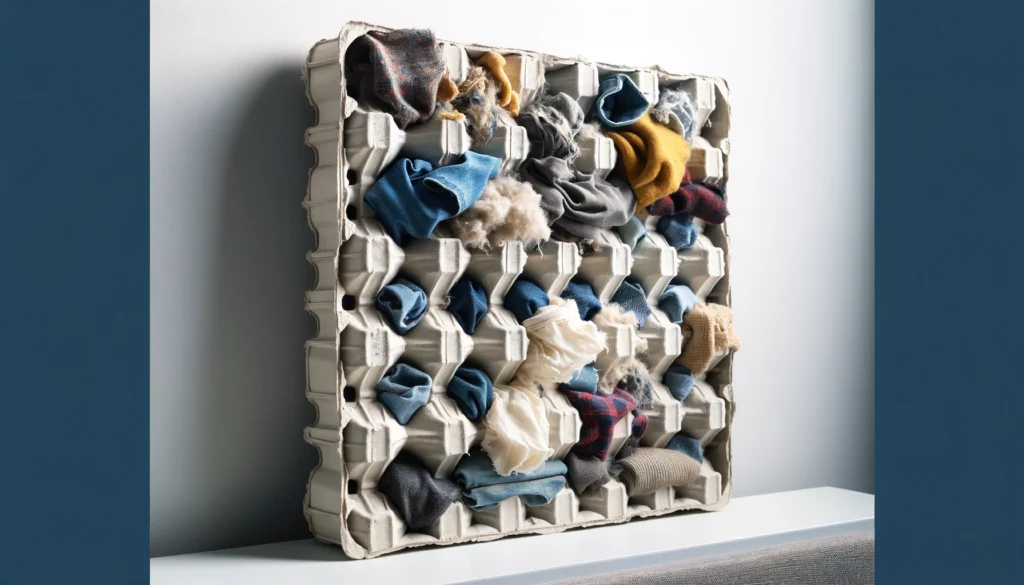
For do-it-yourself sound treatment options, homemade acoustic panels can also easily be constructed by filling the compartments of an egg crate frame with acoustic insulating materials prior to mounting on a wall or ceiling structure.
Pieces of old clothing packed tightly into each grid opening creates cost-effective noise-blocking panels out of recycled textiles.
Any sound-dampening filler forces noise-causing sound waves to permeate deeply into the material rather than freely passing through the thin plastic shell alone.
Other common acoustic treatment alternatives to plain egg crate also include acoustic foam panels or soundproofing foam sheets mounted to room boundaries.
The dense, compressed polymeric construction of these foam noise absorbers allows them to dampen ambient noise effectively via both absorption and barrier methods.
They contain finer pore structures compared to egg crate, enabling enhanced noise capture.
Key Takeaways
In summary, while the open gridwork of egg crate gives it the superficial appearance of a noise-reducing material, plain plastic egg crate provides minimal meaningful acoustic value.
The thin empty ribs fail to capture sound waves and convert their energy, resulting in very little noise absorption or ambient reverberation control.
Effective acoustic materials like insulation, foam, and textiles used in purpose-built acoustic panels contain the physical attributes needed to genuinely dampen sound oscillation.
Constructing your own absorption panels using the frame of egg crate can deliver affordable noise reduction through added sound-dampening filler materials packed inside.
But plain egg crate alone mounted to ceilings or walls supplies insufficient noise absorbing mass and depth required to noticeably reduce overall sound levels.
physics shows us how its hollow lightweight plastic composition allows noise to transmit through the thin plateaued surface as if little barrier exists at all.
Rethink using real acoustic treatment alternatives that actively absorb acoustic energy out of the air rather than mimics that merely diffuse without decibel decreases.
Conclusion
In conclusion, egg crate by itself has limited effectiveness as an acoustic panel material.
While it provides some diffusion, its thin plastic rib structure allows most sound to transmit through without absorption.
For noticeable ambient noise reduction, alternative purpose-built acoustic panels filled with insulating sound-damping materials are better options to explore.
